2009:Robot Design Details: Difference between revisions
From 1511Wookiee
Jump to navigationJump to search
No edit summary |
Drivetrain (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== Drivetrain<br> == | == Drivetrain<br> == | ||
*4-wheel drive | *4-wheel drive(6 if needed)<br> | ||
*Banebots Transmissions | *Four Banebots 12:1 Transmissions | ||
* | *Four 2.5" CIM motors | ||
*Victor 884 [Drive] Speed Controllers | *Victor 884 [Drive] Speed Controllers | ||
*Fixed wheels (slip-style steering)<br> | *Fixed wheels (slip-style steering)<br> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
*27.25” LONG x 37.25” WIDE<br> | *27.25” LONG x 37.25” WIDE<br> | ||
*Rear wheel axis at 5.625 from most rear surfaces (adjustable down to 4.625 corner brace regime permitting) <br> | *Rear wheel axis at 5.625 from most rear surfaces (adjustable down to 4.625 corner brace regime permitting) <br> | ||
*Front wheel axis at 11.625 from front most surfaces (adjustable ± 2.00”) | *Front wheel axis at 11.625 from front most surfaces (adjustable ± 2.00”)<br> | ||
*Using 3/8" bolts to mount bumpers to the frame. See drawing below for bumper mount details. | |||
<br> | *Spacers used will be copper pipe cut to the correct length to space wheels on the axel. | ||
*6 hole patterns in the wheels need to be tapped for 10-32 screws 3/4" deep | |||
*No stiffener element between the wheels seems to be needed. | |||
* | *Trailer hitch is assembled from KOP items. | ||
* | *Determination of need to mount dummy wheels will occur once the top portion of the robot is assembled. | ||
* | *Dummy wheels will be supported using 3/8" bolt, length TBD. | ||
* | *Bearings will be inserted in the dummy wheels from the kit of parts. | ||
* | |||
[[Image:Drivetrain 1-14-2009.JPG|500x400px|Current Drivetrain design as of 01/14/2009]]<br> | [[Image:Drivetrain 1-14-2009.JPG|500x400px|Current Drivetrain design as of 01/14/2009]]<br> | ||
<br> | [[Image:Bumper_Bracket.JPG]]<br> | ||
== Front Ball Entry/Exit == | == Front Ball Entry/Exit == | ||
Revision as of 19:00, 21 January 2009
Main Robot Design
General layout design of the robot, Dimensions ARE NOT exact.
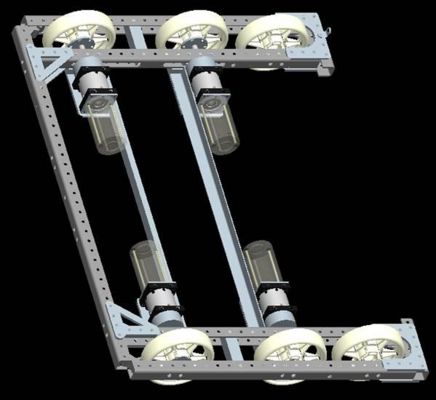
Drivetrain
- 4-wheel drive(6 if needed)
- Four Banebots 12:1 Transmissions
- Four 2.5" CIM motors
- Victor 884 [Drive] Speed Controllers
- Fixed wheels (slip-style steering)
- Banebots encoders on each wheel (http://banebots.com/pc/ELECTRONICS/EN-G0561-KT) -- mounted at transmission outputs.
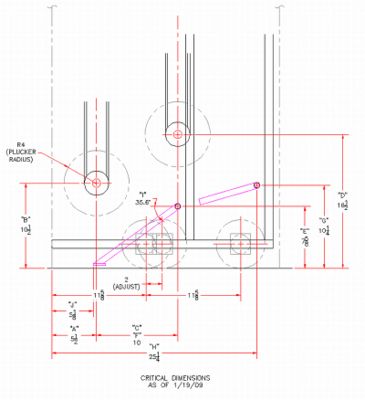
- 27.25” LONG x 37.25” WIDE
- Rear wheel axis at 5.625 from most rear surfaces (adjustable down to 4.625 corner brace regime permitting)
- Front wheel axis at 11.625 from front most surfaces (adjustable ± 2.00”)
- Using 3/8" bolts to mount bumpers to the frame. See drawing below for bumper mount details.
- Spacers used will be copper pipe cut to the correct length to space wheels on the axel.
- 6 hole patterns in the wheels need to be tapped for 10-32 screws 3/4" deep
- No stiffener element between the wheels seems to be needed.
- Trailer hitch is assembled from KOP items.
- Determination of need to mount dummy wheels will occur once the top portion of the robot is assembled.
- Dummy wheels will be supported using 3/8" bolt, length TBD.
- Bearings will be inserted in the dummy wheels from the kit of parts.
Front Ball Entry/Exit
- Ball intake/expulsion power provided by "chicken pluckers" on front conveyor - see conveyor.
- Passage controlled by "door" (TBD - need details)
- Front opening dimensions (TBD)
- Powered by same motor, speed controller as ball hopper trap door (see below).
- Two Limit Switches to tell when door is in open/closed position
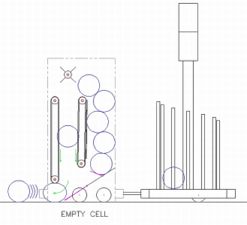
Ball Hopper
- Open top entry for human player introduction
- Entry from conveyor at top of robot; entry controlled by upper ejector
- Exit is a "trap door" at the bottom of the hopper down to the area behind the lower ball collector and at the base of the conveyor system.
- Trap door powered by Nippon Denso Window motor (along with lower collection blocker; possibly a rack & pinion arrangement?)
- Two Limit Switches to tell when door is in open/closed position
- Two Q10RP6R Recievers and Q106E Sources mounted at the top to determine when the hopper is full
- Jaguar speed controller
Ball Conveyor
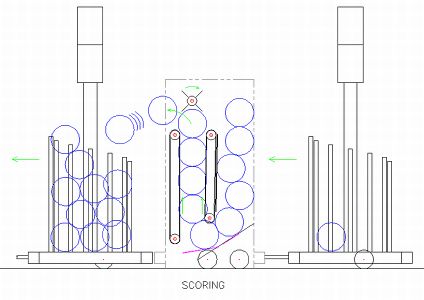
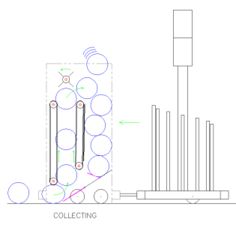
- Two conveyors opposite each other, working together to move balls from ball intake and/or below the ball hopper up to the upper ball ejector/hopper entry point.
- Front conveyor also acts as collector to bring outside balls in via "chicken pluckers" on lower roller of conveyor
- Powered by two independent motors (RS-545 Banebots motors with 25:1 reduction gearboxes)
- Likely NOT direct drive, will likey be chain/sprocket to save space and move weight back on robot
- Banner Sensors (photoelectric): Q10RP6R Reciever and Q106E Source Mounted at the top of conveyor to detect ball "ready to fire"
- 2 Omron photoelectric sensors arranged with a small wheel used to determine conveyor speed. One disk/sensor per conveyor.
- Jaguar speed controller
Upper Ball Ejector
- Spinning ejector directs, based on direction, balls out of robot or in to hopper entry point.
- Powered by Fischer Price 00968-2910 motor with plastic gearbox removed and 25:1 reduction gearbox added (same Banebots units as on conveyor drives)
- Will be chain/sprocket to save space and move weight back on robot, and to allow optimization of ejector speed without loss of motor power
- Shaft encoder sensor (E7P-180-375-S-H-G-3) to monitor rotational speed (180 CPR). Requires 3/8" shaft. If we can't get E7P in time, we may have to use E4P model which requires 1/4" shaft.
- Jaguar speed controller